Place Anti-tank Rounds - Anti-tank weapons are a form of artillery designed to destroy tanks and other armored fighting vehicles, usually from static defensive positions.
The development of special anti-tank ammunition and anti-tank guns was prompted by the appearance of tanks during the First World War.
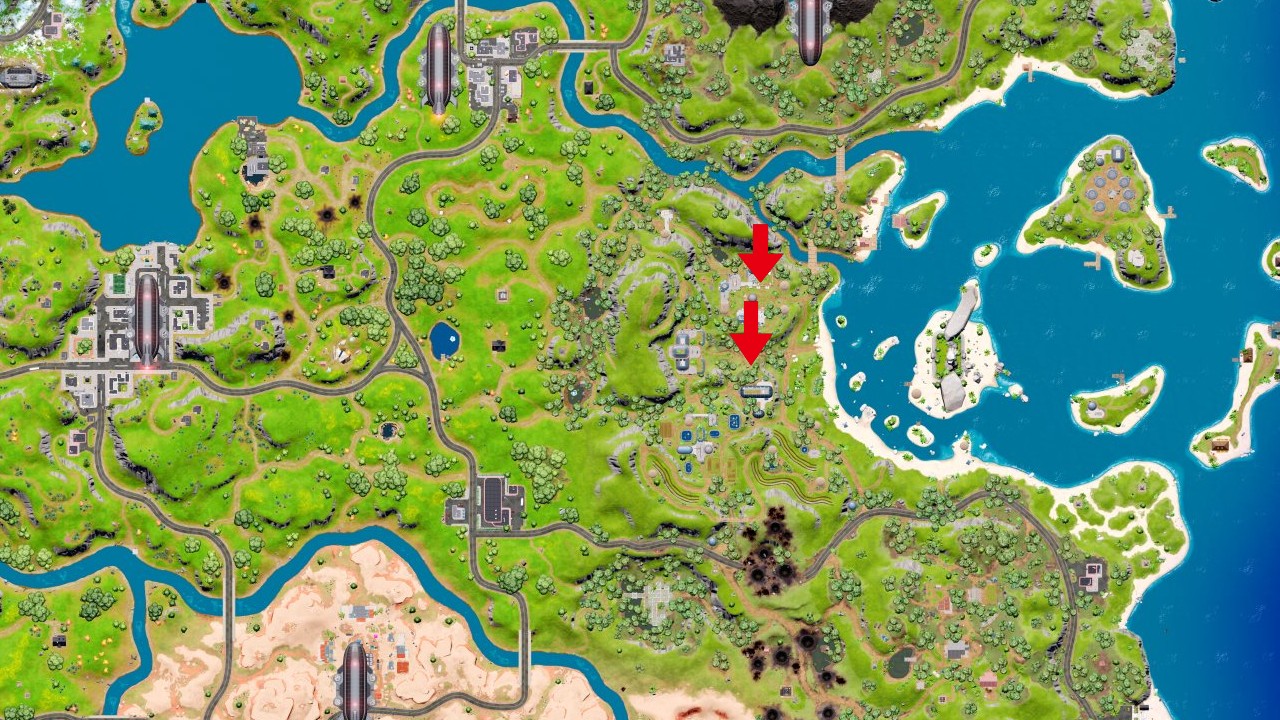
Place Anti-tank Rounds
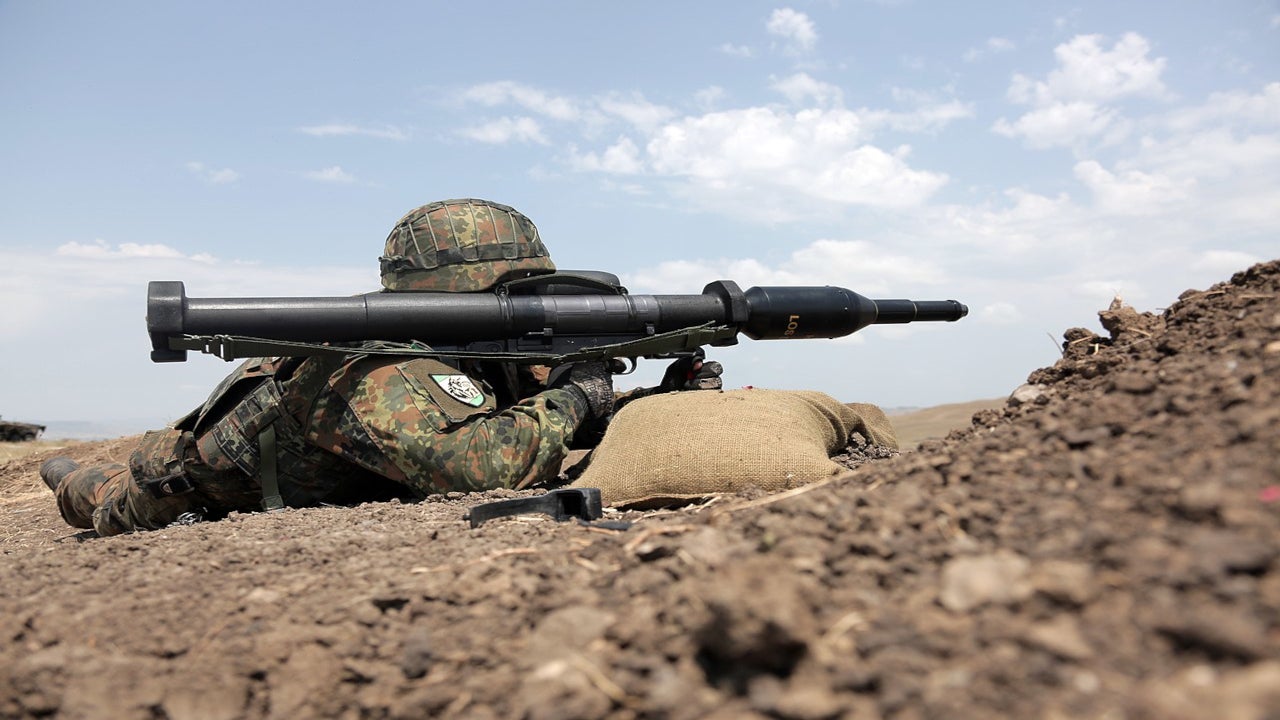

To destroy enemy tanks, artillery often used depressed field guns to fire directly at the target, but this practice released too much valuable ammunition and the effectiveness was limited because the tank's armor was thicker.
Fortnite Place Anti Tank Rounds Guide: Where To Place Anti Tank Rounds
The first special anti-tank artillery began to appear in the 1920s, and during the Second World War it became common in many European armies.
To use the armor, they fired special bullets from the barrel again to achieve a higher muzzle velocity than field guns.
Anti-tank weapons deployed during World War II were often manned by specialist infantry rather than artillery crews, and issued to light infantry units.
The anti-tank guns of the 1920s and 1930s were of small caliber; almost all major armies had it using 37 mm ammunition (the British Army used the slightly larger 40mm 2-pounder gun).
British Self Propelled Anti Tank Gun Archer
As World War II progressed, the appearance of heavier tanks made this weapon obsolete, and anti-tank guns also began to fire larger and more effective rounds. .
The development of the compact charge projectile permanently changed the anti-tank war, because this type of ammunition did not cause a high muzzle velocity and could be fired from light weapons that could be carried of man, like Panzerfaust and American. rifle after rifle without effort.
Although many large-caliber guns were developed during the war that could defeat the most heavily armored tanks, they proved difficult to conceal.

The latest generation of low-recoil anti-tank weapons, which allow projectiles the size of artillery shells to be fired from the shoulder, are considered a more practical option for support in the infantry.
Sdkfz. 191 Kampfpanzer E 50 Ausf. C With X 7 \
The recoilless rifle replaced most conventional anti-tank rifles in the postwar era; However, development of new anti-tank guns with similar recoil continued until the late 1950s in France, Belgium, and the Soviet Union.
The first special anti-tank weapons included anti-tank guns. It arose from the mixed results of deploying field artillery against tanks during World War I, and the need to develop more economical weapons to destroy them.
Most anti-tank guns are more than 1.3 m long, but it is difficult for the infantry to move within the limits of their territory. They can use the tank's armor at some length, but without explosive firepower, usually fail to cause damage, kill, or seriously injure the crew, or kill the tank.
Other infantry support guns designed to defeat difficult targets such as reinforced machine gun emplasemts were used as makeshift anti-tank weapons, including the Frch Canon d'Infanterie de 37 modèle 1916 TRP.
U.s. 37mm Anti Tank (wwii)
The 3.7 cm Tankabwehrkanone 1918 im starrer Räder–lafette was probably the first dedicated anti-tank gun in service. However, the barrel of the gun is based on the Hotchkiss 5 barrel rotary cannon. The 3.7 cm TAK 1918 was designed and built for the German Imperial Army in 1918.
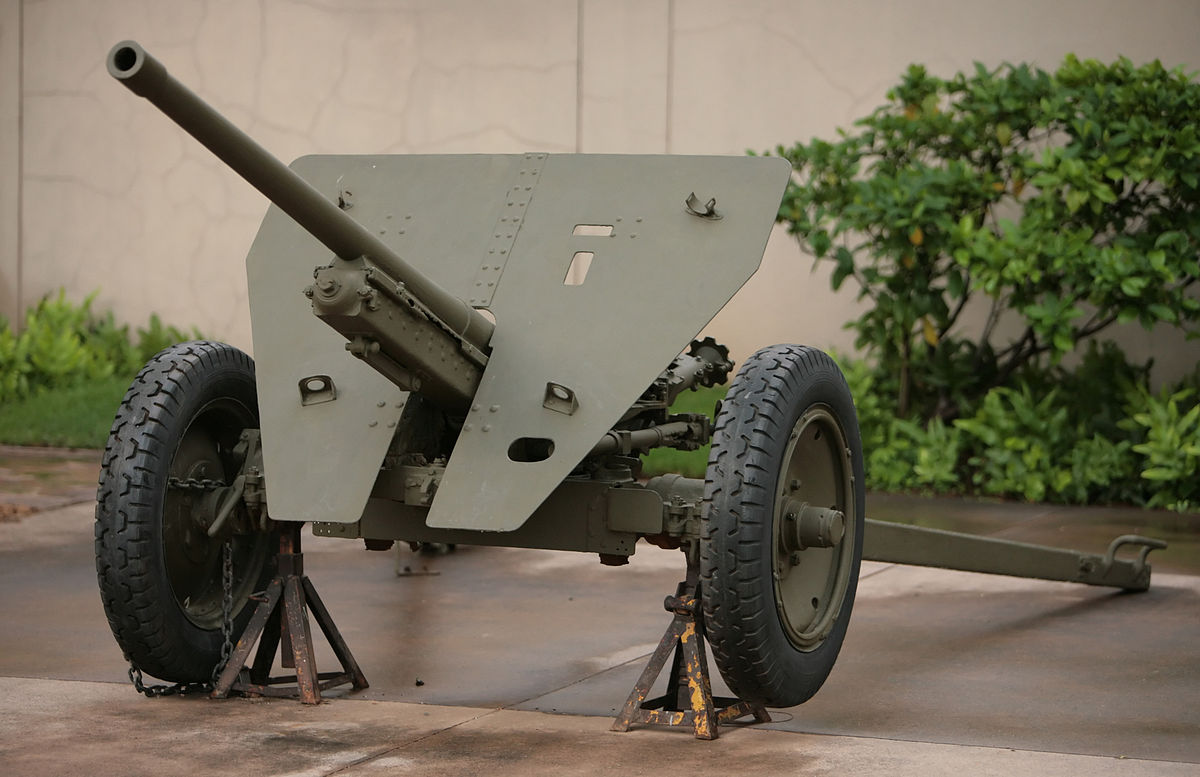
Weighing around 160 kg, the Pak 36 could cause more damage to tanks than using armor plates alone.
A towed gun similar to the Pak 36 was the only anti-tank weapon issued to European armies in the 1930s, and some designs had great influence, such as the Böhler gun.
By the late 1930s, anti-tank guns were being produced by companies in Germany, Austria, France, Czechoslovakia, Belgium, Great Britain, Denmark, and Sweden.
Cm KpÚv Vz. 38
At the start of World War II, most armies adopted light anti-tank guns that fired 3.7 cm (37 mm) rounds.
The weapon is usually mounted on a two-wheeled carriage so that it can be pulled into position, retracted and changed quickly. Since they only weigh a few hundred pounds on average, they can also be placed in position.
All fired a high-explosive and solid armor-piercing shot effective at distances of up to about 500 m, and were increasingly made with gun protection shields in addition to split mounting rails.
They managed to destroy the tanks supplied by both sides in the first two years of the war, but soon proved impott against the heavier tank armor that began in 1940.
Icm 1/35 Pak36 Anti Tank Gun 7.62cm Kit
The Frch doctrine was for the infantry to pass the emy tanks past the accompanying infantry leaving the unsupported tanks to be worked by the anti-tank guns mounted in three echelons. The problem of 58 guns per division gives 10 guns per kilometer of the front expected to overcome emy tanks with a reduction of 50 tanks per kilometer. In the practice of the German invasion of France conctrated tanks in selected divisions to 100 per kilometer.
The introduction of better ammunition and increased muzzle velocity initially helped offset the mediocre performance, but the small-caliber anti-tank gun was clearly outgunned by the more heavily armored tanks.
Medium caliber guns in the 40 to 50 mm range began to appear, some only using rebored 37 mm barrels.

Although they didn't last long either, most of them remained in use in infantry units until the war.
Wwii Era German Dummy Rounds
Anti-tank weapons remained ineffective against flanking armor, as evidenced by an incident in 1941 when a Soviet T-34 tank was hit more than 30 times by a battalion-sized on contingent of German 37 and 50 mm anti-tank guns. The tank was rescued intact and driven back to the line itself a few hours later.
This helped earn the Pak 36 the moniker of Panzeranklopfgerät ("tank door knocker") because the crew opened the presce and threw the shells without damaging the T-34's armor.
Anti-tank gunners began targeting the tank track, or the vulnerable border of the turret ring and gun mantlet, instead of trying to fire lighters against the turret's bow and armor.
These difficulties led to the introduction of new types of ammunition, namely high-altitude anti-tank projectiles (HEAT) and steel disposal sabots (APDS).
What Are The Best Anti Tank Gun Officers In Warpath?
Leading up to World War II, the armor layer was even thicker, with tanks such as the Tiger II equipped with armor over 100 mm thick, compared to the more common 15 mm in 1939.
This led to the development of the third generation of anti-tank guns, large caliber pieces in the 57 to 100 mm range.
The British Army used the Ordnance QF 6-pounder and the Ordnance QF 17-pounder, which was considered a significant improvement in firepower, and the Wehrmacht issued the larger 7.5 cm Pak 41 and 8.8 cm Pak 43.

While the early 37-mm anti-tank guns were easy to store and transport, the larger caliber weapons available at the end of the war required an equally large vehicle to be towed in place, and difficult to hide, dig, drag, or reposition. .
New Release: M1 57mm Anti Tank Gun
By 1945, large anti-tank guns had become almost impractical in their role, and their size and weight were considered a liability.
And although they can defeat the most formidable enemies, most tank units still consist of poorly armored models that remain vulnerable to less expive and more practical guns, as well. Many heavy anti-tank guns were issued, initially, at division level, but gradually to individual infantry battalions.
Meanwhile, the impact of compact hollow warheads was noticed, and some countries began to manufacture man-portable anti-tank weapons using these ammunition.
Development of a portable, shoulder-launched anti-tank rocket launcher began in 1941; most were reloadable, but some, like the German Panzerfaust, were fired from expendable tubes. Unlike anti-tank guns, its light weight makes it easier to move individual infantry on the battlefield, and provides the same level of firepower, but is faster and cheaper to manufacture.
German Anti Tank Gun Pak 40 Municipal Hall Garden
Towed anti-tank weapons disappeared from Western countries, such as the United States, after World War II, replaced by shoulder-fired rocket launchers, recoilless rifles, and eventually, guided anti-tank missiles.
During the war, German engineers proposed new, large-caliber anti-tank guns that used less propellant than rockets or recoilless weapons, but fired the same compact hollow-charge. shells.
German forces then fielded the PAW 600 8 cm, a low-pressure weapon that was lighter in weight and could fire the same type of ammunition as an anti-tank gun at a higher velocity . In the 1950s, the idea was revived by the Belgian company, Mecar, which later improved the concept and developed a low-pressure, smoothbore, 90-mm anti-tank gun.
Due to the low recoil force and light construction, the gun is particularly useful for mounting on armored cars or small gun carriages.
Pennsylvania Jogger Stumbles Upon Anti Tank Round
The design was inspired by the Frch DEFA D921 light-fired anti-tank gun, which fires fin-stabilized shells and is available on a towed carriage or as a vehicle.
The Soviet Union also adopted a similar design at the same time, the 100-mm T-12 anti-tank gun, which fired smooth and fin-stabilized shells.
The Swiss developed their own post-war 90-mm anti-tank weapon, the Pak 50/57, which fired the cannon at a lower velocity than the Mecar or DEFA guns.
With the exception of the T-12, which uses the APDS round, these weapons can only be used with HEAT shells for armor piercing purposes.
Resistance Quest Week 4: Drone, Anti Tank Rounds, And More
The last country known to have produced a dedicated anti-tank rifle was the People's Republic of China in 1988.
The Chinese rifle is known as the Norinco Type 86 and may have been produced as a replacement for the aging T-12.
The anti-tank weapon continues
Anti tank guided missile, tank rounds, anti armor rounds, anti tank vehicle, anti aircraft rounds, anti personnel rounds, best place to buy silver rounds, lego anti tank gun, fuel tank anti siphon, anti tank rounds, 37mm anti personnel rounds, anti tank gun

0 Comments